We are able to offer innovative treatments designed to harness the power of the immune system, helping it to specifically recognise and attack the Lyme disease-causing bacteria. By targeting the underlying cause of the disease rather than just the symptoms, targeted immunotherapies offer a promising solution for patients.
Lyme Disease and Co-infections

Lyme Disease and Co-infections
Restoring Health, One Step at a Time – A combination Therapy Approach
Lyme Disease & Co infections
Unveiling Groundbreaking Therapeutic Treatments
- Targeted Immunotherapies: Revolutionizing Lyme Disease Treatment.
- Beyond Antibiotics: Exploring Alternative Approaches to Lyme Disease Management.
- Integrative Medicine: A Holistic Approach to Lyme Disease Treatment.
Learn why Lyme Disease is difficult to be diagnosed
Lyme Disease and Co-infections are complex medical conditions.
Firstly, one of the main challenges lies in accurately diagnosing these conditions. Lyme Disease, caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi, often presents with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain.
These symptoms can easily be mistaken for other illnesses, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. Co-infections, which are often present alongside Lyme Disease, further complicate the diagnostic process. These co-infections, which include Babesiosis, Bartonella, and Ehrlichiosis, have their own unique set of symptoms and diagnostic tests, making it challenging for healthcare professionals to identify and treat them effectively.
Traditional antibiotic therapy is the standard treatment for Lyme Disease, but its effectiveness can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience a complete resolution of symptoms, while others may continue to experience chronic symptoms despite treatment. Additionally, co-infections may require different treatment approaches, further complicating the management of these conditions. Another challenge is the limited understanding of the long-term effects of Lyme Disease and co-infections. While acute Lyme Disease is well-documented, there is still much to learn about the chronic manifestations of the disease and its associated co-infections

Service Overview
We use synergistic therapies that concentrate on removing biological and environmental contaminants,
boosting immune system activity, and a number of methods to treat infections directly.
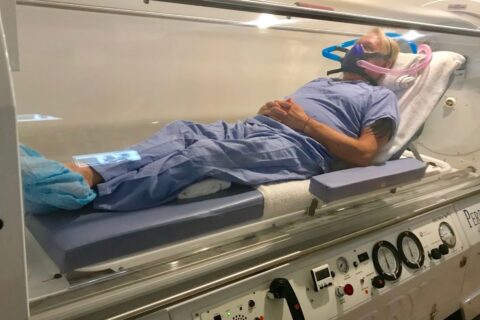
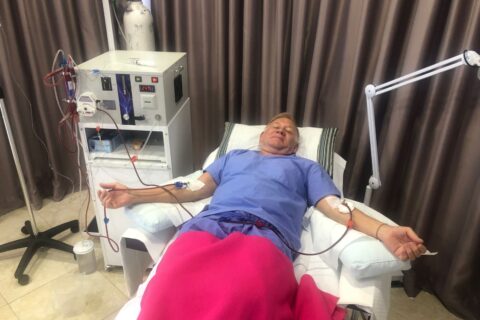
HBOT (Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy) and EBOO (extracorporeal Blood Oxygenation and Ozonation) therapies are two treatment approaches used for Lyme Disease and co-infections, where HBOT involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber to enhance oxygen delivery to tissues and boost the immune system, and eBOO utilizes ozonated blood to kill pathogens, improve oxygenation, and stimulate the immune response.
Oxygen therapy involves providing patients with a concentrated supply of oxygen, which helps to boost their immune system and fight off the bacteria causing Lyme disease. This therapy can be administered in various ways, such as through an oxygen mask or through hyperbaric chambers. The increased oxygen levels in the body promote healing and reduce inflammation, providing relief to patients suffering from the symptoms of Lyme disease.
EBOO ozone therapy, on the other hand, utilizes ozone molecules to target and eliminate the bacteria responsible for Lyme disease. Ozone has powerful antimicrobial properties, and when introduced into the body, it can help to eradicate the infection. This therapy can be administered through various methods, including intravenous infusion or direct injection into affected joints or muscles.
-
Functional Medicine
Functional medicine offers a promising treatment protocol by focusing on optimizing immune function, reducing inflammation, and supporting the body’s natural healing processes.
-
Telehealth
We offer remote diagnostics, consultation and prescriptions via Live Video connection with our Telemedicine doctors which are licensed and trained for a number of conditions.
-
Consultation and Diagnostics
Following a medical assessment and our discussions and evaluations, we create a personalized programme and recommend additional therapies to compliment treatments.
-
Individual Recovery Care Plans
Custom recovery plans that’s right for you. We understand the importance of educating you on the most effective ways to take care of your body so that you can heal quickly.
-
Alternative Therapies
We offer alternative therapies as a non-conventional approach to treat various ailments or enhance overall well-being, ranging from practices like acupuncture, herbal medicine, chiropractic care, yoga, meditation, and homeopathy, among others.
-
Nutritionist
Our nutritionists are an important component of your treatment because they provide guidance and expertise in developing personalized nutritional plans, addressing and preventing nutritional deficiencies, and promoting overall health and well-being.
-
Anticoagulation Therapy
In certain cases, we will recommend but safely use anticoagulants or blood thinners in order to treat patients who’ve experienced blood clots in either the veins or the arteries and have also experienced a number of cardiovascular diseases.
-
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy and rehabilitation programmes designed to enhance performance both physically and mentally, increase ATP production, accelerate recovery time from injuries, reduce lactic acid build-up in the tissues and de-stress the body.
Available Treatments
- HELP Apheresis
- Plasmapheresis
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
- EBOO / Ozone Therapy
- IV Therapy
- Red Light Therapy
Supportive Treatments
- Cryotherapy
- FIR Sauna
- Lymphatic Drainage Massage
- Ozone Colonics
Please message on WhatsApp +61 418 909 826
Or contact us via email form below
Other Services
We Focus On Your Level of Whole Body Health In Order to Help You Fully Heal Your Body…From The Inside Out!

Lyme Disease and Co-infections
Restoring Health, One Step at a Time – A combination Therapy Approach
Two Powerful Types of Stem Cells Therapies
Harnessing the Potential of Stem Cells for Advanced Therapies

Long Covid and Post Vaccine Syndrome
Unlock the path to recovery with our specialised treatments

Treatment for Autoimmune Conditions
Revive Your Body’s Balance with Our Autoimmune Conditions Treatments